
|
|
 |
|
 |
||
|
Introduction In SAS programming, a common task is to combine observations from two or more data sets into a new data set. Using the DATA step, you can combine data sets in several ways, including the following: |
| Method of Combining | Illustration |
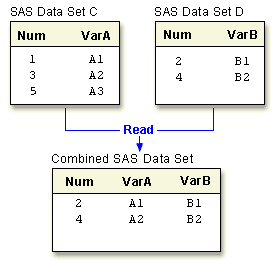
| One-to-one reading
Creates observations that contain all of the variables from each contributing data set. Combines observations based on their relative position in each data set. Statement: SET |
 |
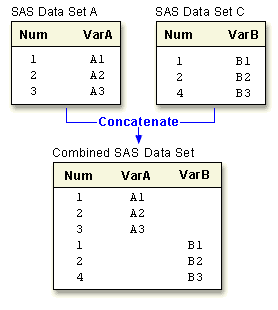
| Concatenating
Appends the observations from one data set to another. Statement: SET |
 |
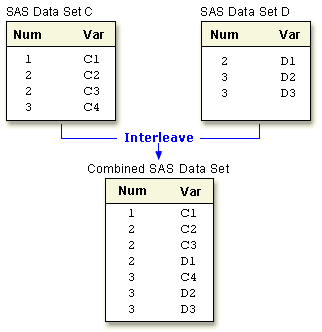
| Interleaving Intersperses observations from two or more data sets, based on one or more common variables. Statements: SET, BY |
 |
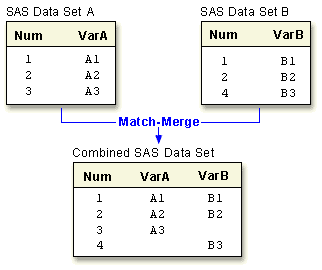
| Match-merging Matches observations from two or more data sets into a single observation in a new data set according to the values of a common variable. Statements: MERGE, BY |
 |
| You can also use PROC SQL to join data sets according to common values. PROC SQL enables you to perform many other types of data set joins. See the SQL Processing with SAS e-learning course for additional training. |
|
This lesson shows you how to combine SAS data sets using one-to-one reading, concatenating, interleaving, and match-merging. When you use the DATA step to combine data sets, you have a high degree of control in creating and manipulating data sets. |
Time to CompleteThis lesson contains pages and takes approximately 2 hours to complete. |
ObjectivesIn this lesson, you learn to
|
PrerequisitesBefore taking this lesson, you should complete the following lessons:
|
| Copyright
© 2003 SAS Institute Inc.,
Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved. Terms of Use & Legal Information | Privacy Statement |
||